The Global Economy
Teacher Resources
Driving Question: Is globalization making the world more equal or increasing inequality?
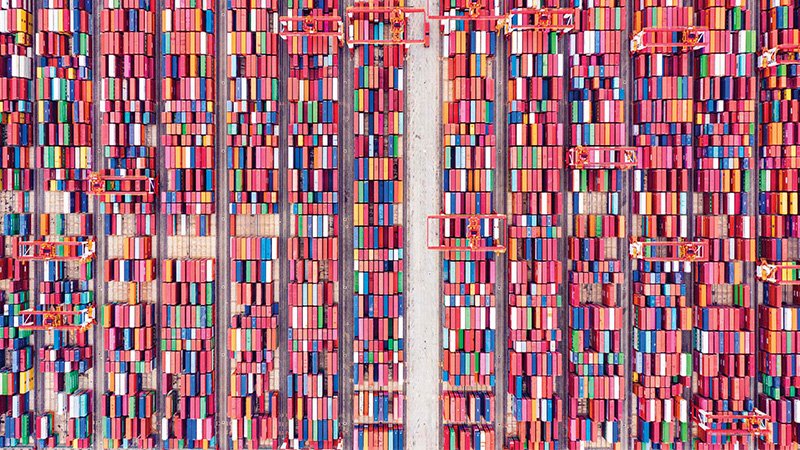
Where does the stuff we use come from, and who benefits from the production and distribution of these goods? This lesson follows the paths of goods, money, and migration to uncover how the global economy impacts lives in very different ways.
Learning Objectives:
- Use evidence to evaluate the effects of globalization through the production and distribution frame.
- Use a graphic biography to support, extend, or challenge the overarching narratives of this period.
Vocab Terms:
- consumption
- globalization
- gross domestic product (GDP)
- liberalize
- multinational
- outsource
- regulation
Opener: The Global Economy
To teach this lesson step, refer to page 2 of the Lesson 9.3 Teaching Guide.
Globalization has knit our world together in a complex web of connections. Can you trace the links across the globe?
Global Production
Interview with a Robot
- Students interview an AI agent about its past. In particular, they should explore what people, places, and products were needed for the AI agent to exist. As they conduct the interview, students should create a list of:
- Material components that allow the AI to function.
- Where material components are made and moved to.
- The companies and people involved in the AI agent’s creation.
- The resources the AI uses to maintain its functions.
- Once the interview is over, students should use their notes to create a global map of their AI agent, marking all relevant locations, people, and things that are part of its creation and functioning.
What does this do? As an extension of the Follow the Product activity, this interview will help students understand the massive amounts of resources and complexity needed for this simple interaction to occur. It will provide them with new evidence about the intricacies and connections of globalization and prepare them to grapple with questions about the Anthropocene.
Global production links people, places, and economies in surprising ways. Investigate how goods move across borders and what their journeys reveal about labor, trade, and inequality in the global economy.
-
Guiding Questions
-
Before you read
Preview the questions below, and then skim the article. Be sure to look at the section headings and any images.
While you read
Look for answers to these questions:
- How does cheap labor affect global trade?
- How has automation changed the US job market?
- Why does Apple rely on skilled workers in China?
- What are conflict minerals?
- Why is it hard to know if products are ethically made?
After you read
Respond to this question: How has globalization changed labor and culture over time? Use evidence from the article to support your answer.
Uneven Globalization
To teach this lesson step, refer to page 5 of the Lesson 9.3 Teaching Guide.
Looking for more ideas about how to teach historical comics? Check out the Graphic Biographies Guide.
Globalization doesn’t affect everyone the same way. With these materials, you’ll see where opportunities are concentrated and how people respond through migration and adaptation.
-
Guiding Questions
-
Before you read
Preview the questions below, and then skim the article. Be sure to look at the section headings and any images.
While you read
Look for answers to these questions:
- What does Thomas Friedman argue about globalization?
- What forces drove the different stages of globalization?
- How does Richard Florida respond to Friedman’s ideas?
- How does Florida use cities to support his argument?
- What critique does Dr. Vandana Shiva offer?
After you read
Respond to this question: What are some ways that the distribution of power in your school is flat or spiky?
-
Guiding Questions
-
Before you read
Preview the questions below, and then skim the comic, paying attention to things like prominent colors, shapes, and types of text and fonts. How do you know where to start and in which direction to read? What’s in the gutters (the space between panels)? Who or what is the focus of the comic?
While you read
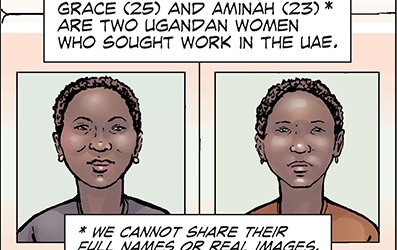
- Why did Grace and Aminah leave Uganda for work in the UAE?
- How did they get permission to travel?
- How were their experiences in the UAE different?
- How did the Ugandan government respond to stories like Aminah’s?
- How does the artwork highlight their different experiences?
After you read
Respond to this question: How does this biography support or challenge what you’ve learned about how globalization affects different communities?
Webs of Globalization
To teach this lesson step, refer to page 7 of the Lesson 9.2 Teaching Guide.
Curious to see images of how this activity looks in the classroom? Read the Community Forum thread, Our Interconnected World – Small Class Size? for some visual ideas on how to weave this activity into the classroom.
Globalization has knit our world together in ways that affect how we live, work, and connect. Reading about it is one thing, but seeing it is another! Explore the concept of globalization through movement, visuals, and reflection to better understand how our world is deeply interconnected.
Closer: The Global Economy
To teach this lesson step, refer to page 9 of the Lesson 9.3 Teaching Guide.
Take a look at the Openers and Closers Guide to find out more about why these important activities bookend our lessons.
What have you learned about the effects of globalization? Is the world flattening or is inequality spiking?
Globalization Up Close
To teach this lesson step, refer to page 9 of the Lesson 9.3 Teaching Guide.
From everyday life on Dollar Street to China’s global rise and voices from around the world, these resources add new layers to your understanding of global inequality and connection.
-
Guiding Questions
-
Before you read
Preview the questions below, and then skim the article. Be sure to look at the section headings and any images.
While you read
Look for answers to these questions:
- What economic changes happened in China after 1949?
- What were the goals and outcomes of the Great Leap Forward?
- What were the goals and outcomes of the Cultural Revolution?
- What policies did Deng Xiaoping introduce after Mao’s death?
- How has China balanced economic change with political control?
After you read
Respond to this question: Do you think “socialism with Chinese characteristics” is just capitalism under one-party rule? Use evidence from the article to support your answer.