The Economy in the Interwar Period
Teacher Resources
Driving Question: How did different governments around the world respond to economic crisis after 1900?
How did a stock market crash in the US lead to a global economic depression? Investigate how the interconnection of the world that began in the fifteenth century and intensified throughout the long nineteenth century led to an international economic crisis. Nations responded to the Great Depression in different ways, but in many regions this depression made the state more powerful. And in some places, governments turned to authoritarianism.
Learning Objectives
- Explain how different governments responded to economic crises after 1900.
- Investigate the similarities and differences between the political ideologies of communism and fascism.
- Use the historical thinking skill of contextualization to understand the economic and political circumstances that contributed to economic crises after 1900.
- Analyze primary source documents to evaluate the economic crises and how governments responded to them in the interwar period.
Vocab Terms:
- authoritarianism
- dictator
- economic stagnation
- fascism
- racism
- totalitarianism
- welfare state
Opener: The Economy in the Interwar Period
To teach this lesson step, refer to page 3 of the Lesson 7.4 Teaching Guide.
Students who can parse questions may have a leg up on the AP Exam. Read more in the Community thread, Exam reviews that worked for my students with Janet Mann.
Ever read a prompt you just didn’t understand? We’ve got you covered with the Question Parsing Tool!
Contextualization: The Great Depression
To teach this lesson step, refer to page 3 of the Lesson 7.4 Teaching Guide.
Students need feedback to learn—use the Contextualization Feedback Form to help students reflect and improve upon their contextualization skills.
Capitalism and globalization both played a role in the Great Depression—but how? Find out in this activity!
Global Great Depression
To teach this lesson step, refer to page 7 of the Lesson 7.4 Teaching Guide.
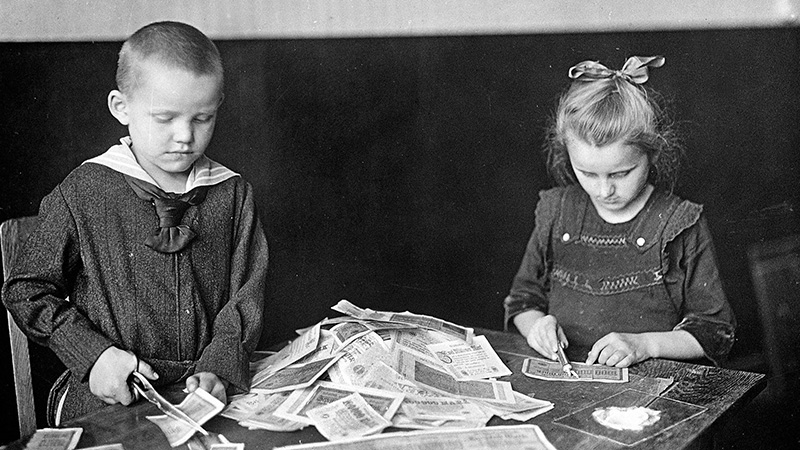
The 1929 stock market crash triggered a global economic collapse due to the interdependence among various industrialized national economies. In response to the crash, many countries turned inward, increased colonial exploitation, and expanded state control—paving the way for authoritarian regimes in some regions.
-
Guiding Questions
-
Before you read
Preview the questions below, and then skim the article. Be sure to look at the section headings and any images.
While you read
Look for answers to these questions:
- Why did the Great Depression spread from the United States to so many other parts of the world so quickly?
- How did governments react to the crisis?
- Why was the crisis so devastating for Latin America and for European colonies in Africa and Asia?
- In what ways did some states grow more powerful during the crisis?
- What ended the Great Depression?
After you read
Respond to the following questions:- To what extent does this article explain how different governments responded to economic crises after 1900?
- Can you draw any comparison between more recent economic crises and the crisis in the 1930s?
- The Great Depression was a collapse of international networks and global economic systems. What are some ways that these collapses reshaped social interactions and organization?
Source Collection: Economy in the Interwar Period
To teach this lesson step, refer to page 9 of the Lesson 7.4 Teaching Guide.
Different nations had different responses to the economic uncertainty in the Interwar period. These primary sources will help you understand those responses. As you read the primary source excerpts in this collection, use the accompanying Quick-Sourcing Tool and activity to guide your analysis.
Communism in the Soviet Union
To teach this lesson step, refer to page 9 of the Lesson 7.4 Teaching Guide.
Under Joseph Stalin, Soviet Russia became a major world power and played a key role in defeating Nazi Germany. However, Stalin’s rule was marked by brutal authoritarianism, including mass deaths and the use of forced labor camps, making the USSR a prime example of totalitarianism in the 20th century.
-
Guiding Questions
-
Before you read
Preview the questions below, and then skim the article. Be sure to look at the section headings and any images.
While you read
Look for answers to these questions:
- What big challenges did Lenin and the Bolshevik (communist) leadership face in the first stages of their revolution?
- How does the author characterize the Bolshevik party during the early part of their rule?
- How did Stalin’s rise to power change the way the Bolsheviks ruled?
- What were some consequences for everyday life under the Soviet command economy?
- How were fascism and communism under Stalin similar and different?
After you read
Respond to the following questions:
- Think about the last time you heard someone called a “communist” or a “fascist”. Do you think the term was used correctly?
- In this unit we see the rise of governments that have certain political characteristics. We call these characteristics fascism, authoritarianism, and totalitarianism. Using these definitions, evaluate which of these terms can appropriately be applied to Stalin’s Soviet Union. It may be all, some, or none:
- A totalitarian regime has a highly centralized system of government that requires strict obedience.
- An authoritarian regime focuses on the maintenance of order at the expense of personal freedom.
- A fascist regime is a government that embraces extreme nationalism, violence, and action with the goal of internal cleansing and external expansion.
Closer: The Economy in the Interwar Period
To teach this lesson step, refer to page 11 of the Lesson 7.4 Teaching Guide.
Unpacking visuals is critical in today’s world. Read more in the Visual Literacy in the Classroom! Community thread.
You’ve learned a lot about the global economy between the world wars. Now, analyze a cartoon to assess how one nation responded.