Interwar Ideologies
Teacher Resources
Driving Question: Why did extremist ideologies like fascism emerge during the interwar period?
After World War I, the world was in crisis. In this lesson, you’ll explore how economic collapse, fear, and political uncertainty gave rise to extreme ideologies—like fascism, communism, and authoritarianism—and how people across the globe responded to these new visions of power and order.
Learning Objectives:
- Use the historical thinking practice of contextualization to evaluate the circumstances that led to the global depression.
- Use the historical thinking practices of comparison and causation to analyze the rise of authoritarian governments in various regions of the world.
- Use a graphic biography to support, extend, or challenge the overarching narratives of this period.
Vocab Terms:
- authoritarianism
- communism
- fascism
- Great Depression
- internationalism
- isolationism
- nationalization
- totalitarianism
Opener: Interwar Ideologies
To teach this lesson step, refer to page 3 of the Lesson 8.5 Teaching Guide.
Openers are great for activating prior knowledge and getting students engaged in learning. Read more in the OER Project Openers and Closer Guide.
As you get ready to examine extremist ideologies, step into the shoes of a citizen watching their nation fall to pieces.
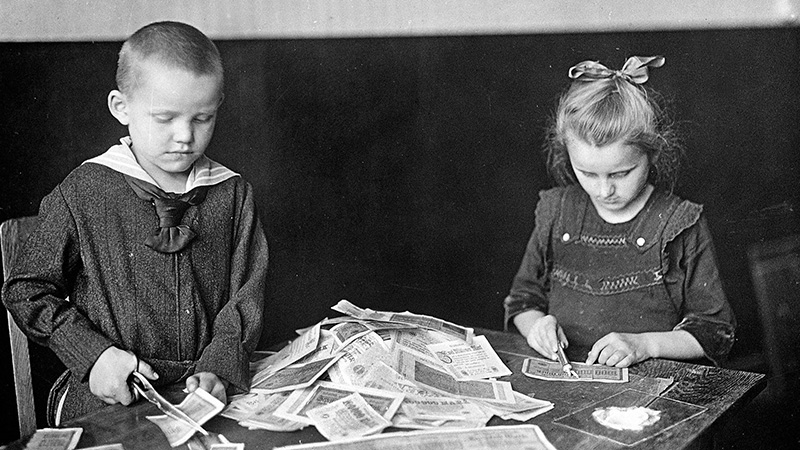
The Great Depression
To teach this lesson step, refer to page 3 of the Lesson 8.5 Teaching Guide.
Students need feedback to learn—use the Contextualization Feedback Form to help students reflect and improve upon their contextualization skills.
Explore the global causes and consequences of the Great Depression. Through a contextualization activity and an in-depth article, you'll see how economic interdependence and political decisions led to a worldwide crisis that set the stage for significant historical developments.
-
Guiding Questions
-
Before you read
Preview the questions below, and then skim the article. Be sure to look at the section headings and any images.
While you read
Look for answers to these questions:
- Why did the Great Depression spread beyond the United States so quickly?
- How did governments respond to the crisis?
- Why was the Depression especially devastating for Latin America and European colonies?
- How did some governments gain more power during this time?
- What brought the Great Depression to an end?
After you read
Respond to these questions: Can crisis bring out unity in a community? What examples from the Great Depression support your thinking?
Competing Ideologies
To teach this lesson step, refer to page 8 of the Lesson 8.5 Teaching Guide.
While war is not unusual in history, it can still be triggering for many. Think about how to approach these topics with your students by taking a look this resource on Teaching Sensitive Topics in Social Studies.
After the Great Depression, people were searching for answers—and leaders offered a wide range of them. Use these materials to learn what fascism is, how authoritarian governments gained power, and how some groups tried to resist through international cooperation. Then, you’ll analyze a political party platform to understand how extremist messages appealed to people facing crisis and uncertainty.
-
Guiding Questions
-
Before you watch
Preview the questions below, and then review the transcript.
While you watch
Look for answers to these questions:
- What is the origin of the word fascism?
- Why is it useful to define fascism as a political behavior?
- How do fascists gain and maintain power?
- Why did fascists see internationalism as a threat?
- What makes total war important to fascist ideology?
After you watch
Respond to these questions: Which ideas or methods of fascism are similar to systems you’ve seen earlier in the course, such as imperialism or absolutism? How are they different?
Key Ideas
-
Guiding Questions
-
Before you read
Preview the questions below, and then skim the article. Be sure to look at the section headings and any images.
While you read
Look for answers to these questions:
- What actions showed Mussolini’s foreign policy was aggressive?
- How did Germany and Italy justify their expansion?
- How did Japan explain its imperial expansion?
- What did the authoritarian regimes of Italy, Germany, Japan, and the USSR have in common?
- What were some ways the authoritarian regimes of Italy, Germany, Japan, and the USSR were different?
After you read
Respond to this question: Why do you think so many people supported authoritarian or fascist governments, even when those governments used violence and repression?
-
Guiding Questions
-
Before you watch
Preview the questions below, and then review the transcript.
While you watch
Look for answers to these questions:
- What did the Kellogg-Briand Pact try to achieve?
- What were some efforts at international cooperation in the 1920s?
- How does internationalism in the 1920s compare to earlier attempts in history?
- Why did the League of Nations struggle to succeed?
- What lasting impact, if any, did the Kellogg-Briand Pact have?
After you watch
Respond to this question: How does the failure of internationalism challenge or support the networks frame narrative?
Key Ideas
Closer: Interwar Ideologies
To teach this lesson step, refer to page 11 of the Lesson 8.5 Teaching Guide.
Still looking for support for students in reading Graphic Biographies? Take about 9 minutes to watch how to Decode a Graphic Biography.
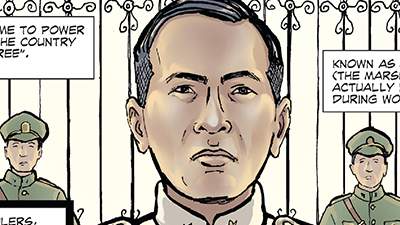
Plaek Phibunsongkhram’s leadership in Thailand shows that fascist and authoritarian ideas spread far beyond Europe. His actions reveal how local leaders adapted extreme ideologies to meet their own goals, helping us understand why these movements gained global appeal during the interwar years.
-
Guiding Questions
-
Before you read
Preview the questions below, and then skim the comic, paying attention to things like prominent colors, shapes, and types of text and fonts. How do you know where to start and in which direction to read? What’s in the gutters (the space between panels)? Who or what is the focus of the comic?
While you read
- Why did Plaek Phibunsongkhram rename his country Thailand?
- What is one policy that shows Phibunsongkhram’s authoritarian rule?
- Why did he promote pad thai?
- What happened to Phibunsongkhram after the war?
- How does the design of the biography show that Phibunsongkhram was an authoritarian leader?
After you read
Respond to this question: How does this biography of Phibunsongkhram support or challenge what you’ve learned about authoritarianism and fascism during the interwar period.
Facing the Downturn
To teach this lesson step, refer to page 11 of the Lesson 8.5 Teaching Guide.
Explore how people around the world faced economic challenges during the interwar period. These sources reveal the diverse ways communities experienced and responded to the Great Depression.
Fascism, Communism, and Authoritarianism
To teach this lesson step, refer to page 12 of the Lesson 8.5 Teaching Guide.
Why did so many countries turn to extremist leaders in the interwar years? These articles add valuable global context by examining how fascism, communism, and authoritarianism took root in Italy, the Soviet Union, and Japan. These cases help you compare how different systems responded to crisis—and why so many people supported strong, often repressive, governments.
-
Guiding Questions
-
Before you read
Preview the questions below, and then skim the article. Be sure to look at the section headings and any images.
While you read
Look for answers to these questions:
- How did Hitler use the Reichstag fire to his advantage?
- How did he make his rise to power seem legal?
- What early steps did the Nazis take against German Jews?
- Why were the Nuremberg Laws significant?
- What did the Nazis gain by targeting Jewish people?
After you read
Respond to this question: How did the Nazi regime make extreme actions seem acceptable to ordinary people in the 1930s?
-
Guiding Questions
-
Before you read
Preview the questions below, and then skim the article. Be sure to look at the section headings and any images.
While you read
Look for answers to these questions:
- What did it take for the Fascists to defeat the Socialists in Italy?
- What were two ways Fascism grew in the Po Valley?
- Why were some Fascists disappointed with Mussolini early on?
- What actions did Mussolini take to strengthen his rule?
- How was Italian Fascism’s view of race different from Nazi Germany’s?
After you read
Respond to this question: Why do you think Mussolini had less control over Italy than Hitler had over Germany?
-
Guiding Questions
-
Before you read
Preview the questions below, and then skim the article. Be sure to look at the section headings and any images.
While you read
Look for answers to these questions:
- What challenges did Lenin and the Bolsheviks face early on?
- How did the Bolsheviks exercise control over politics and society?
- How did Stalin’s leadership change the way the USSR was governed?
- What effects did the Soviet command economy have on everyday life?
- In what ways was communism under Stalin similar to fascism?
After you read
Respond to this question: In what ways did the government under Stalin affect the role of communities in the USSR?
-
Guiding Questions
-
Before you read
Preview the questions below, and then skim the article. Be sure to look at the section headings and any images.
While you read
Look for answers to these questions:
- How did Japan model its government after Bismarck’s Germany?
- Why was military independence from civilian leadership important for Japan’s expansion?
- What steps did Japan take that made it a fascist or authoritarian state?
- How did Japan’s economy change under government control?
After you read
Respond to this question: What actions could a society take to limit the rise of authoritarian leaders like those seen in Japan during the interwar period?