The Silk Roads
Teacher Resources
Driving Question: How have the trade routes known as the Silk Roads expanded and contracted over time?
Despite the name, the Silk Roads carried much more than silk, and they consisted of much more than roads. Intricate networks of trade and many different merchants traveling over land and sea moved goods across Afro-Eurasia. But they also carried more than just material goods. The Silk Roads brought technologies, cultures, and religions to new places.
Learning Objectives:
- Analyze how the collapse and recovery of empires affected the spread of belief systems and the expansion of trade networks like the Silk Roads.
- Use the historical thinking practice of continuity and change over time to evaluate historical events and processes.
Vocab Terms:
- administrative
- aristocracy
- caravan
- cocoon
- immunity
- initiative
- restructure
Opener: The Silk Roads
To teach this lesson step, refer to page 2 of the Lesson 5.6 Teaching Guide.
What did Europeans think about Marco Polo and his discoveries? Use your critical-thinking skills to find out.
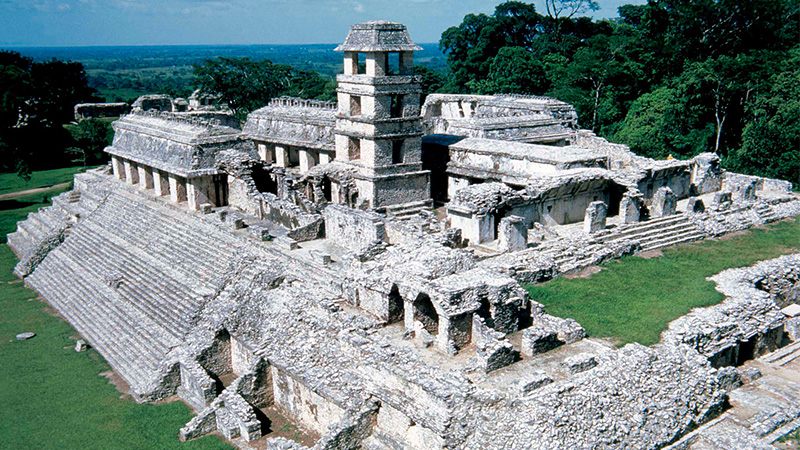
Silk Road Merchants
To teach this lesson step, refer to page 3 of the Lesson 5.6 Teaching Guide.
OER Project partnered with NYU to learn more about the Silk Roads. Learn more about Diverse Perspectives on the Silk Roads: The Sogdians here.
How were the Silk Roads responsible for connecting the diverse societies of Afro-Eurasia? Find out in the article below and then explore further in the simulation.
-
Guiding Questions
-
Before you read
Preview the questions below, and then skim the article. Be sure to look at the section headings and any images.
While you read
Look for answers to these questions:
- Why is the Afro-Eurasian system of long-distance trade described as an archipelago?
- What was the effect of the Mongol Empire on trade?
- What role did this regional trade network play in helping Johannes Gutenberg create his printing press?
- What impact did annual fairs have on the European economy?
- What was one negative effect of interconnected trade?
After you read
Respond to this question: This article is about production and distribution in Afro-Eurasia. Does it leave any groups of people out of this story of production and distribution?
Rebuilding Networks
To teach this lesson step, refer to page 7 of the Lesson 5.6 Teaching Guide.
Want to know more about OER Project’s approach to CCOT? Take a look at this one-pager.
-
Guiding Questions
-
Before you watch
Preview the questions below, and then review the transcript.
While you watch
Look for answers to these questions:
- The term Silk Road is commonly used. Why is that name somewhat misleading?
- What were some of the commonly traded items on the Silk Roads?
- How did the Han Dynasty “manage” the Silk Roads? What were the economic impacts of this management?
- What was the impact of the fall of the Han Dynasty on the Silk Roads?
- What is the Chinese Belt and Road Initiative?
After you watch
Respond to this question: The Tang Dynasty created a golden age across the Silk Roads, starting in 626 CE, but the Tang Dynasty gained power in 618 CE. What does this suggest about the effects of collapse and recovery on large networks?
The Silk Roads didn’t collapse after the fall of the Han Dynasty. They continued to tie together local networks and boost economic production across Asia.
Key Ideas
-
Guiding Questions
-
Before you read
Preview the questions below, and then skim the article. Be sure to look at the section headings and any images.
While you read
Look for answers to these questions:
- How did the growth of imperial power expand trade?
- What were the Pax Sinica and Pax Romana, and how did they impact trade?
- Why were camels the best way for traders to move their goods on land?
- What was the role of women in silk production, and why is that role significant?
- What were some things the Silk Roads spread without even trying?
After you read
Respond to this question: What would you expect to happen along the Silk Roads during a period in which the Roman Empire, and then the Han Dynasty, collapsed? Use evidence to support your thinking.
Closer: The Silk Roads
To teach this lesson step, refer to page 10 of the Lesson 5.6 Teaching Guide.
Closers like this are a great opportunity to informally assess student understanding. Read more in the OER Project Assessment Guide.
One of the best ways to learn is by teaching someone else. In this quick closing activity, you’ll test your classmate’s knowledge about the Silk Roads.
Sources of Collapse
To teach this lesson step, refer to page 10 of the Lesson 5.6 Teaching Guide.
Use these sources to see how trade affected communities by examining words written by the people involved.