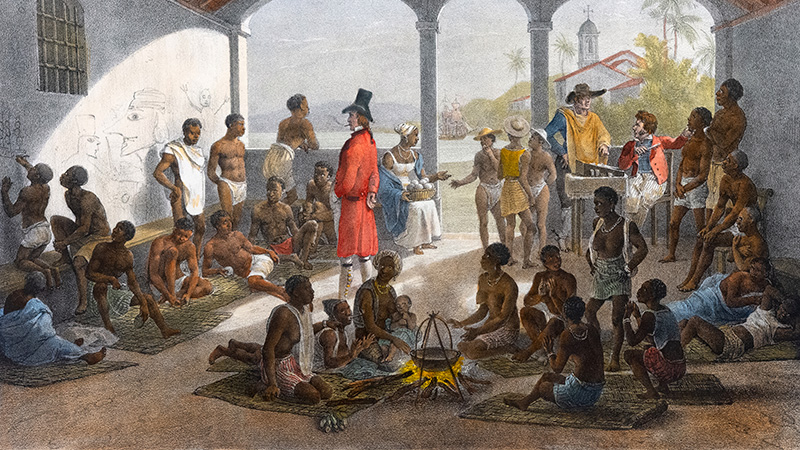
The Transatlantic Slave Trade
The transatlantic slave trade was one of history’s greatest crimes—a massive theft of human life that fueled colonization and shaped the modern world. Our classroom-ready lessons help students trace this global system from European capitals to African coasts and the plantations of the Americas. Along the way, they’ll uncover the human cost, the economic impact, and the lasting consequences of a trade that changed everything.
 How to Teach the Transatlantic Slave Trade
How to Teach the Transatlantic Slave Trade

Teaching Sensitive Topics
Get support for difficult but meaningful discussions about the transatlantic slave trade.

Blog: Teaching challenging topics in social studies
Two veteran teachers reflect on teaching challenging topics and how they help students build historical empathy.

Blog: Dive in with National Geographic Explorer Tara Roberts
Show students the legacy of the transatlantic slave trade through human stories and experiences.

Blog: Zumbi: King of Palmares and Bane of the Slavers
Zumbi of Palmares was one the many enslaved people who challenged colonial power in 17th-century Brazil.
Lessons Plans on The Transatlantic Slave Trade
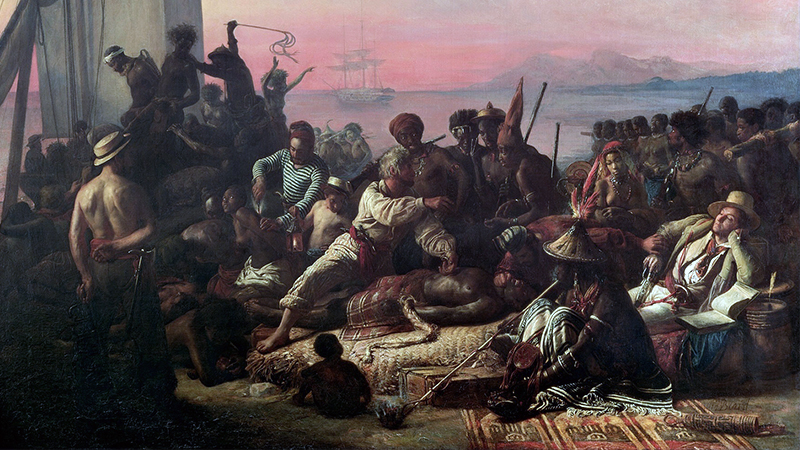

Lesson 3.6
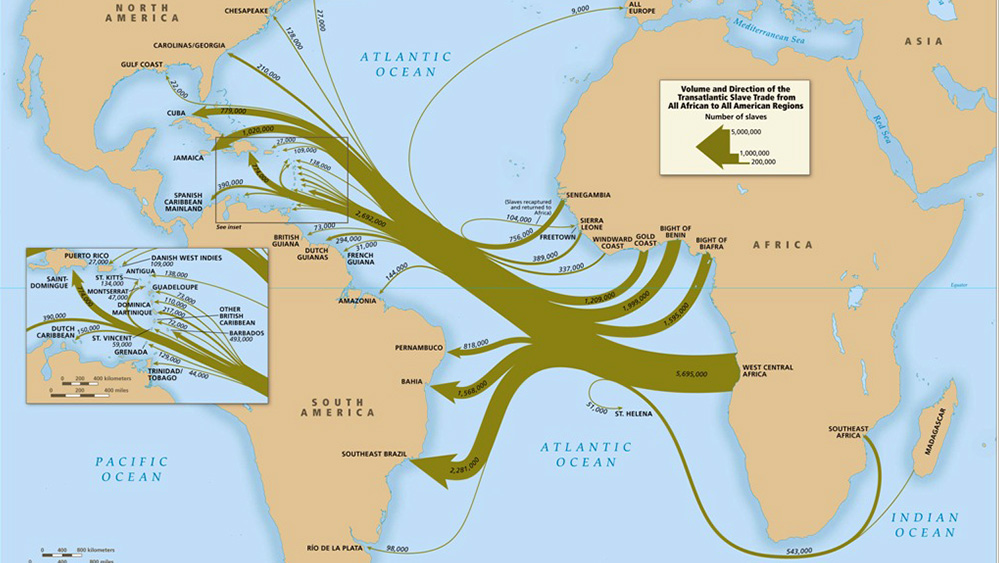
The Transatlantic Slave Trade
For 400 years, over 12 million people were enslaved and forcibly transported to the Americas, where they worked in horrific conditions. Their labor enriched European empires and settler colonies.
View Lesson
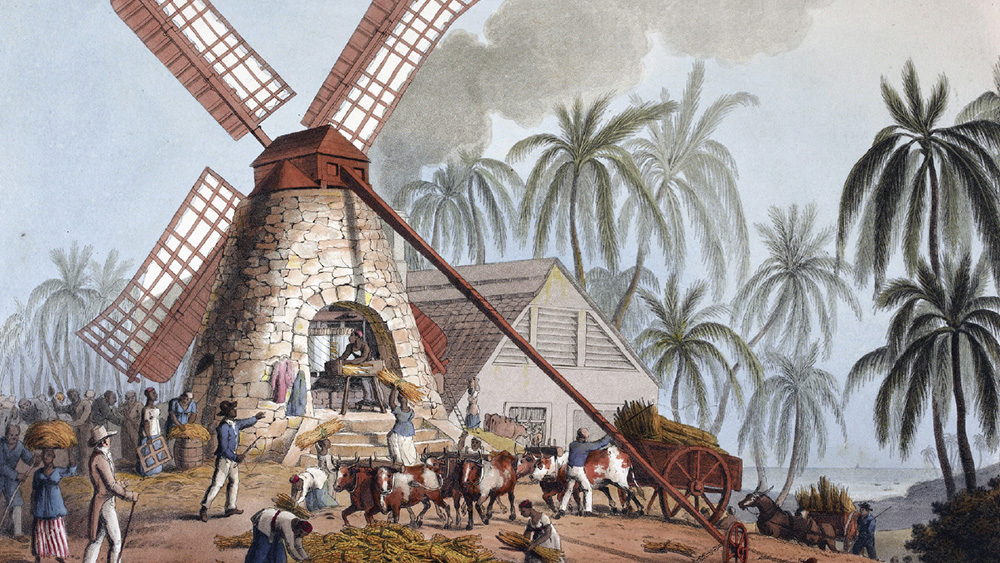
Lesson 3.7
The Plantation System
Humans build communities to share goods, beliefs, and ideas across networks. While fourteenth-century connections spread innovations, they also brought challenges like the devastating Black Death.
View Lesson
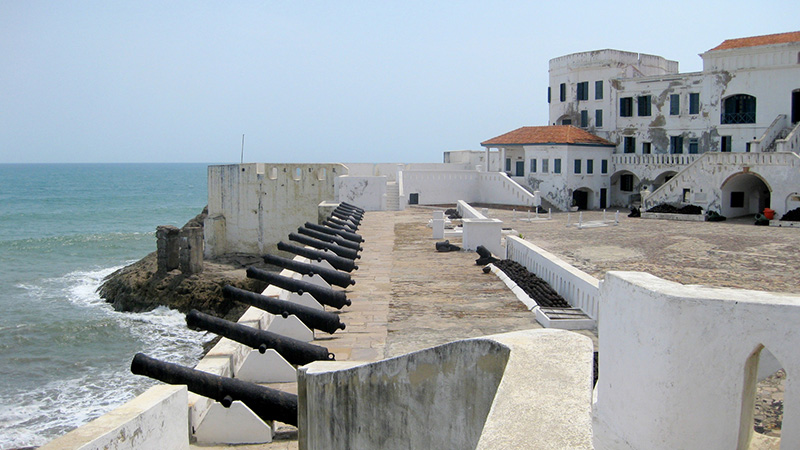

Lesson 6.9.3
The Middle Passage
In this video, comic, and activity, we adjust our lenses to focus on a small region in Africa and the life of one enslaved man to better understand how the slave trade affected the entire continent.
View Lesson
Transatlantic Slave Trade Resources for Deeper Learning
Impact of the Slave Trade: Through a Ghanaian Lens
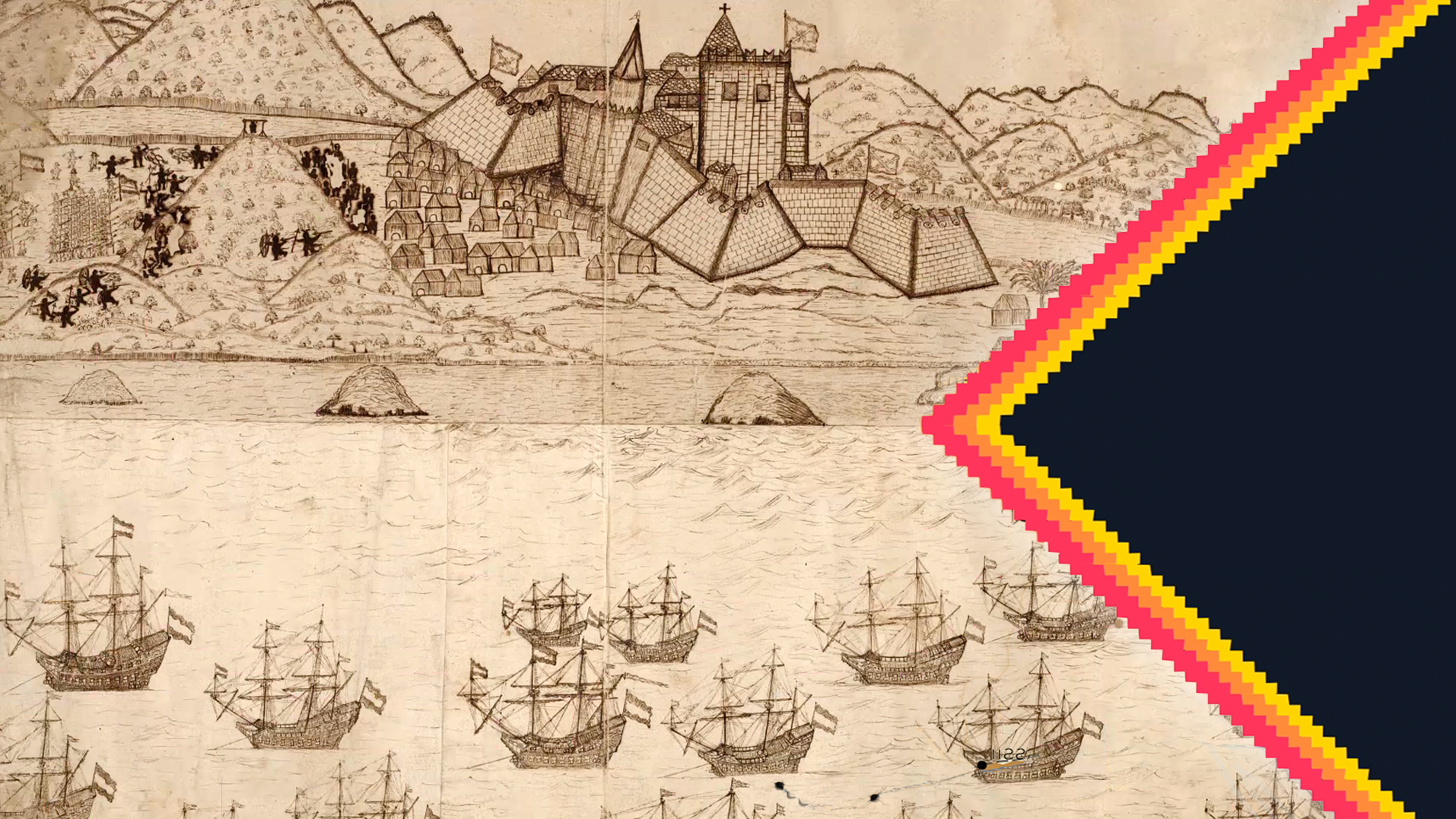

Video
Impact of the Slave Trade: Through a Ghanaian Lens
How did the Atlantic slave trade impact communities in Africa? This video focuses on experiences of people in Ghana to reveal bigger truths about this transoceanic system.
Empires, Enslavement, and Revolutions Thematic Map
Visual Aid
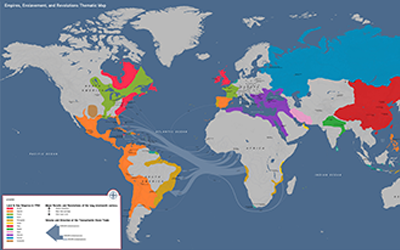
Empires, Enslavement, and Revolutions Thematic Map
A full-color thematic map of Empires, Enslavement, and Revolutions in 1750 CE, meant to help you support, extend, and challenge the frame narratives.
Domingos Álvares

Graphic Biographies
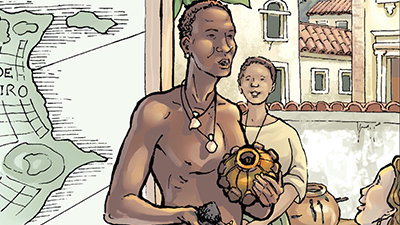
Domingos Álvares
As a priest and healer, Domingos Álvares was dedicated to building communities and networks wherever he went.
Capitalism and Slavery

Article
Capitalism and Slavery
Slaving and slavery existed alongside capitalism. But were they rival economic systems? Or did they support each other?
Curating the Past

Activity
Curating the Past
If you were a museum curator, how would you design exhibits to help people understand the importance of the transatlantic slave trade?
Source Collection: First Person Accounts - Transatlantic Slave Trade
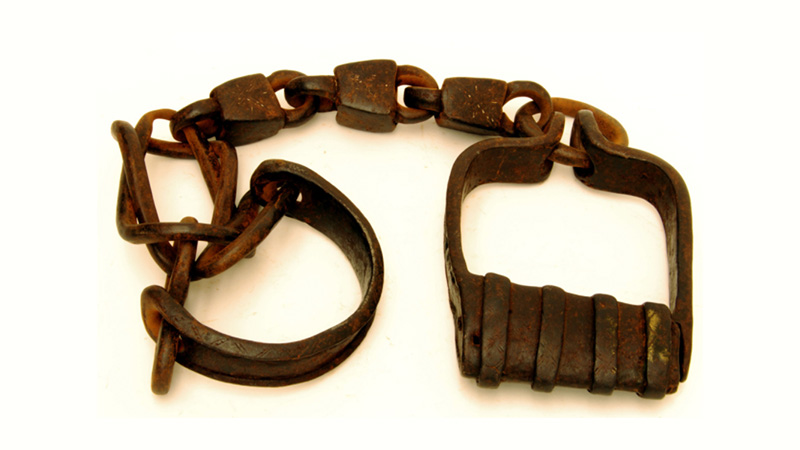

Article
Source Collection: First Person Accounts - Transatlantic Slave Trade
Over 12.5 million people were enslaved and transported across the Atlantic Ocean. These first-hand accounts show the horrors of the journey and some ways people resisted.

Community: Ask, Connect, Share
Join a community of world history teachers for help teaching tough topics like enslavement and the slave trade.
